Quickstart¶
Installation¶
You can install connexion using pip:
$ pip install connexion
Connexion provides ‘extras’ with optional dependencies to unlock additional features:
flask: Enables theFlaskAppto build applications compatible with the Flask ecosystem.swagger-ui: Enables a Swagger UI console for your application.uvicorn: Enables to run the your application usingapp.run()for development instead of using an external ASGI server.
You can install them as follows:
$ pip install connexion[<extra>]
$ pip install connexion[<extra1>,<extra2>].
Creating your application¶
Connexion can be used either as a standalone application or as a middleware wrapping an existing
ASGI (or WSGI) application written using a different framework. The standalone application can be
built using either the AsyncApp or FlaskApp.
The
AsyncAppis a lightweight application with native asynchronous support. Use it if you are starting a new project and have no specific reason to use one of the other options.The
FlaskAppleverages the Flask framework, which is useful if you’re migrating from connexion 2.X or you want to leverage the Flask ecosystem.The
ConnexionMiddlewarecan be wrapped around any existing ASGI or WSGI application. Use it if you already have an application written in a different framework and want to add functionality provided by connexion
from connexion import AsyncApp
app = AsyncApp(__name__)
View a detailed reference of the options accepted by the AsyncApp
- class connexion.AsyncApp(import_name: str, *, lifespan: Optional[Callable[[Any], AbstractAsyncContextManager]] = None, middlewares: Optional[list] = None, specification_dir: Union[Path, str] = '', arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None)
Connexion Application based on ConnexionMiddleware wrapping a async Connexion application based on starlette tools.
- Parameters:
import_name – The name of the package or module that this object belongs to. If you are using a single module, __name__ is always the correct value. If you however are using a package, it’s usually recommended to hardcode the name of your package there.
lifespan – A lifespan context function, which can be used to perform startup and shutdown tasks.
middlewares – The list of middlewares to wrap around the application. Defaults to
middleware.main.ConnexionMiddleware.default_middlewaresspecification_dir – The directory holding the specification(s). The provided path should either be absolute or relative to the root path of the application. Defaults to the root path.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – Instance of
options.ConnexionOptionswith configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAP.security_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERS
Note
To leverage the FlaskApp, make sure you install connexion using the
flask extra.
from connexion import FlaskApp
app = FlaskApp(__name__)
View a detailed reference of the options accepted by the FlaskApp
- class connexion.FlaskApp(import_name: str, *, lifespan: Optional[Callable[[Any], AbstractAsyncContextManager]] = None, middlewares: Optional[list] = None, server_args: Optional[dict] = None, specification_dir: Union[Path, str] = '', arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None)
Connexion Application based on ConnexionMiddleware wrapping a Flask application.
- Parameters:
import_name – The name of the package or module that this object belongs to. If you are using a single module, __name__ is always the correct value. If you however are using a package, it’s usually recommended to hardcode the name of your package there.
lifespan – A lifespan context function, which can be used to perform startup and shutdown tasks.
middlewares – The list of middlewares to wrap around the application. Defaults to
middleware.main.ConnexionMiddleware.default_middlewaresserver_args – Arguments to pass to the Flask application.
specification_dir – The directory holding the specification(s). The provided path should either be absolute or relative to the root path of the application. Defaults to the root path.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
swagger_ui_options – A
options.ConnexionOptionsinstance with configuration options for the swagger ui.pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – Instance of
options.ConnexionOptionswith configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAP.security_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERS
from asgi_framework import App
from connexion import ConnexionMiddleware
app = App(__name__)
app = ConnexionMiddleware(app)
You can also wrap a WSGI application leveraging the a2wsgi.WSGIMiddleware:
from wsgi_framework import App
from connexion import ConnexionMiddleware
from a2wsgi import WSGIMiddleware
wsgi_app = App(__name__)
asgi_app = WSGIMiddleware(wsgi_app)
app = ConnexionMiddleware(asgi_app)
View a detailed reference of the options accepted by the
ConnexionMiddleware
- class connexion.ConnexionMiddleware(app: Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any], Callable[[], Awaitable[MutableMapping[str, Any]]], Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any]], Awaitable[None]]], Awaitable[None]], *, import_name: Optional[str] = None, lifespan: Optional[Callable[[Any], AbstractAsyncContextManager]] = None, middlewares: Optional[List[Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any], Callable[[], Awaitable[MutableMapping[str, Any]]], Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any]], Awaitable[None]]], Awaitable[None]]]] = None, specification_dir: Union[Path, str] = '', arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None)
The main Connexion middleware, which wraps a list of specialized middlewares around the provided application.
- Parameters:
import_name – The name of the package or module that this object belongs to. If you are using a single module, __name__ is always the correct value. If you however are using a package, it’s usually recommended to hardcode the name of your package there.
middlewares – The list of middlewares to wrap around the application. Defaults to
middleware.main.ConnexionmMiddleware.default_middlewaresspecification_dir – The directory holding the specification(s). The provided path should either be absolute or relative to the root path of the application. Defaults to the root path.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – Instance of
options.ConnexionOptionswith configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAP.security_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERS.
Registering an API¶
While you can register individual routes on your application, connexion really shines when you register an API defined by an OpenAPI (or Swagger) specification.
run.py
def post_greeting(name: str):
return f"Hello {name}", 200
app.add_api("openapi.yaml")
openapi.yaml
openapi: "3.0.0"
...
paths:
/greeting/{name}:
post:
operationId: run.post_greeting
responses:
200:
content:
text/plain:
schema:
type: string
parameters:
- name: name
in: path
required: true
schema:
type: string
The operation described in your specification is automatically linked to your Python view function
via the operationId. You can change this behavior using different Resolvers, see
Routing. When the endpoint is called, connexion will take care of routing, security,
request body and parameter parsing, and response serialization. All based on the specification.
You can add as many APIs as you want to a single application. The add_api() method
provides a lot of configuration options. When an option is provided both to the App and the API,
the API value will take precedence.
View a detailed reference of the options accepted by the add_api() method
- connexion.AsyncApp.add_api(self, specification: Union[Path, str, dict], *, base_path: Optional[str] = None, name: Optional[str] = None, arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None, **kwargs) Any
Register an API represented by a single OpenAPI specification on this application. Multiple APIs can be registered on a single application.
- Parameters:
specification – OpenAPI specification. Can be provided either as dict, a path to file, or a URL.
base_path – Base path to host the API. This overrides the basePath / servers in the specification.
name – Name to register the API with. If no name is passed, the base_path is used as name instead.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – A
options.ConnexionOptionsinstance with configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAPsecurity_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERSkwargs – Additional keyword arguments to pass to the add_api method of the managed middlewares. This can be used to pass arguments to middlewares added beyond the default ones.
- Returns:
The Api registered on the middleware application wrapping the framework.
- connexion.FlaskApp.add_api(self, specification: Union[Path, str, dict], *, base_path: Optional[str] = None, name: Optional[str] = None, arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None, **kwargs) Any
Register an API represented by a single OpenAPI specification on this application. Multiple APIs can be registered on a single application.
- Parameters:
specification – OpenAPI specification. Can be provided either as dict, a path to file, or a URL.
base_path – Base path to host the API. This overrides the basePath / servers in the specification.
name – Name to register the API with. If no name is passed, the base_path is used as name instead.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – A
options.ConnexionOptionsinstance with configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAPsecurity_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERSkwargs – Additional keyword arguments to pass to the add_api method of the managed middlewares. This can be used to pass arguments to middlewares added beyond the default ones.
- Returns:
The Api registered on the middleware application wrapping the framework.
- connexion.ConnexionMiddleware.add_api(self, specification: Union[Path, str, dict], *, base_path: Optional[str] = None, name: Optional[str] = None, arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None, **kwargs) None
Register een API represented by a single OpenAPI specification on this middleware. Multiple APIs can be registered on a single middleware.
- Parameters:
specification – OpenAPI specification. Can be provided either as dict, a path to file, or a URL.
base_path – Base path to host the API. This overrides the basePath / servers in the specification.
name – Name to register the API with. If no name is passed, the base_path is used as name instead.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – A dict with configuration options for the swagger ui. See
options.ConnexionOptions.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAPsecurity_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERSkwargs – Additional keyword arguments to pass to the add_api method of the managed middlewares. This can be used to pass arguments to middlewares added beyond the default ones.
- Returns:
The Api registered on the wrapped application.
Running your application¶
You can run your application using an ASGI server such as uvicorn. If you defined your
app in a python module called run.py, you can run it as follows:
# assuming your application is defined as ``app`` in ``run.py``
$ uvicorn run:app
Or with gunicorn (which is recommended in production).
# assuming your application is defined as ``app`` in ``run.py``
$ gunicorn -k uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker run:app
See the uvicorn documentation for more details or check this overview of available ASGI servers for other options.
If you installed connexion using connexion[uvicorn], you can run it using the
run method. This is only recommended for development:
app.run()
To leverage automatic reloading of your application, you need to provide the application as an import string. In most cases, this can be achieved as follows:
from pathlib import Path
app.run(f"{Path(__file__).stem}:app")
View a detailed reference of the options accepted by the run() method
- connexion.AsyncApp.run(self, import_string: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)
Run the application using uvicorn.
- Parameters:
import_string – application as import string (eg. “main:app”). This is needed to run using reload.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to uvicorn.run.
- connexion.FlaskApp.run(self, import_string: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)
Run the application using uvicorn.
- Parameters:
import_string – application as import string (eg. “main:app”). This is needed to run using reload.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to uvicorn.run.
- connexion.ConnexionMiddleware.run(self, import_string: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)
Run the application using uvicorn.
- Parameters:
import_string – application as import string (eg. “main:app”). This is needed to run using reload.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to uvicorn.run.
The Swagger UI¶
If you installed connexion using the swagger-ui extra, a Swagger UI is available for each
API, providing interactive documentation. By default the UI is hosted at {base_path}/ui/
where base_path` is the base path of the API.
https://{host}/{base_path}/ui/
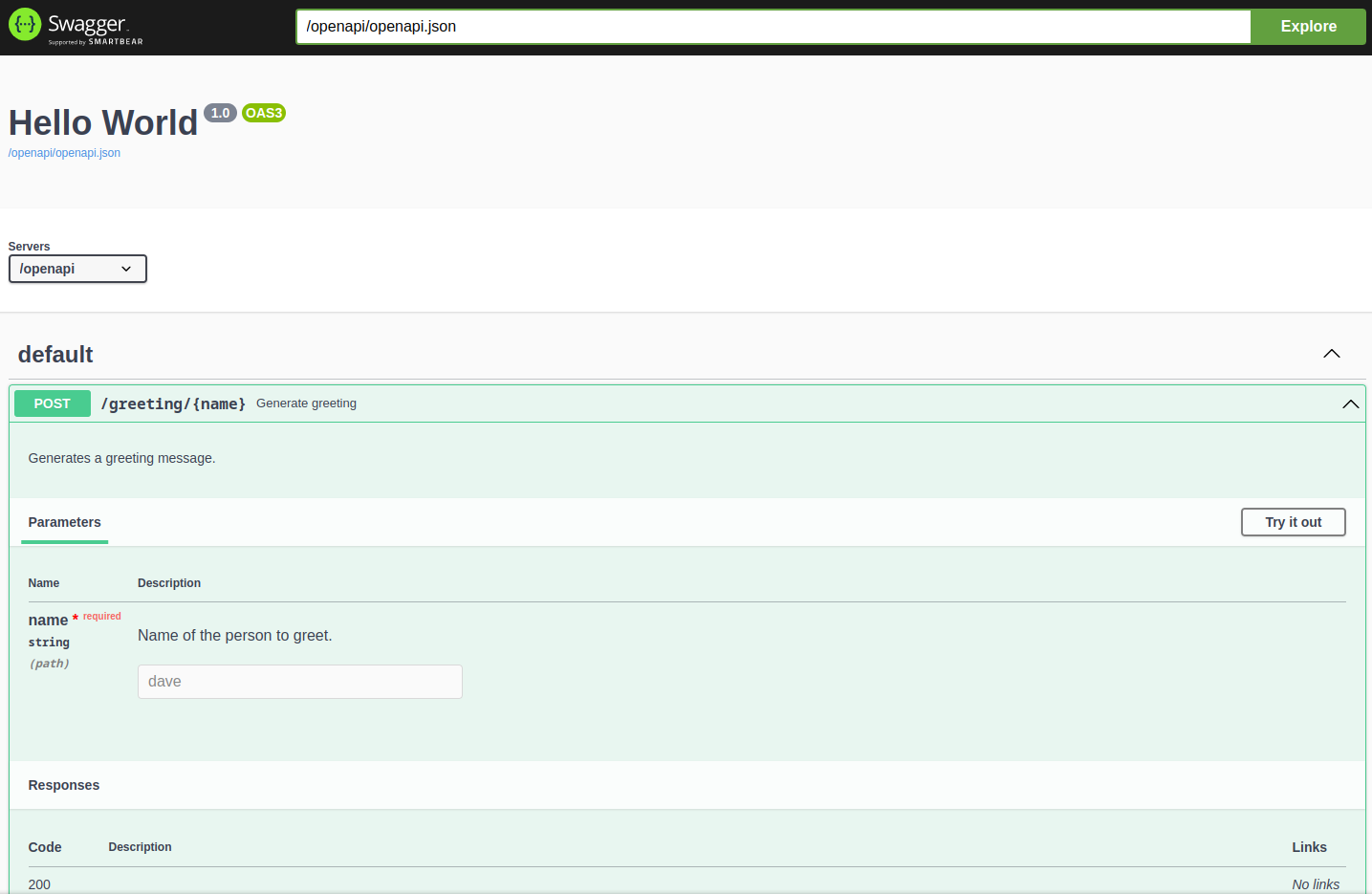
Check The Swagger UI for information on how to configure the UI.
Full App class reference¶
For more details on what you can do, view the complete API reference below.
View a detailed reference of the AsyncApp
- class connexion.AsyncApp(import_name: str, *, lifespan: Optional[Callable[[Any], AbstractAsyncContextManager]] = None, middlewares: Optional[list] = None, specification_dir: Union[Path, str] = '', arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None)¶
Connexion Application based on ConnexionMiddleware wrapping a async Connexion application based on starlette tools.
- Parameters:
import_name – The name of the package or module that this object belongs to. If you are using a single module, __name__ is always the correct value. If you however are using a package, it’s usually recommended to hardcode the name of your package there.
lifespan – A lifespan context function, which can be used to perform startup and shutdown tasks.
middlewares – The list of middlewares to wrap around the application. Defaults to
middleware.main.ConnexionMiddleware.default_middlewaresspecification_dir – The directory holding the specification(s). The provided path should either be absolute or relative to the root path of the application. Defaults to the root path.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – Instance of
options.ConnexionOptionswith configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAP.security_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERS
- add_api(specification: Union[Path, str, dict], *, base_path: Optional[str] = None, name: Optional[str] = None, arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None, **kwargs) Any¶
Register an API represented by a single OpenAPI specification on this application. Multiple APIs can be registered on a single application.
- Parameters:
specification – OpenAPI specification. Can be provided either as dict, a path to file, or a URL.
base_path – Base path to host the API. This overrides the basePath / servers in the specification.
name – Name to register the API with. If no name is passed, the base_path is used as name instead.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – A
options.ConnexionOptionsinstance with configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAPsecurity_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERSkwargs – Additional keyword arguments to pass to the add_api method of the managed middlewares. This can be used to pass arguments to middlewares added beyond the default ones.
- Returns:
The Api registered on the middleware application wrapping the framework.
- add_error_handler(code_or_exception: Union[int, Type[Exception]], function: Callable[[ConnexionRequest, Exception], Union[Awaitable[ConnexionResponse], ConnexionResponse]]) None¶
Register a callable to handle application errors.
- Parameters:
code_or_exception – An exception class or the status code of HTTP exceptions to handle.
function – Callable that will handle exception, may be async.
- add_middleware(middleware_class: Type[Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any], Callable[[], Awaitable[MutableMapping[str, Any]]], Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any]], Awaitable[None]]], Awaitable[None]]], position: MiddlewarePosition = MiddlewarePosition.BEFORE_CONTEXT, **options: Any) None¶
Add a middleware to the stack on the specified position.
- Parameters:
middleware_class – Middleware class to add
position – Position to add the middleware, one of the MiddlewarePosition Enum
options – Options to pass to the middleware_class on initialization
- add_url_rule(rule, endpoint: Optional[str] = None, view_func: Optional[Callable] = None, **options)¶
Connects a URL rule. Works exactly like the route decorator.
Basically this example:
@app.route('/') def index(): pass
Is equivalent to the following:
def index(): pass app.add_url_rule('/', 'index', index)
Internally`route` invokes add_url_rule so if you want to customize the behavior via subclassing you only need to change this method.
- Parameters:
rule – the URL rule as string.
endpoint – the name of the endpoint for the registered URL rule, which is used for reverse lookup. Flask defaults to the name of the view function.
view_func – the function to call when serving a request to the provided endpoint.
options – the options to be forwarded to the underlying
werkzeug.routing.Ruleobject. A change to Werkzeug is handling of method options. methods is a list of methods this rule should be limited to (GET, POST etc.). By default a rule just listens for GET (and implicitly HEAD).
- route(rule: str, **options)¶
A decorator that is used to register a view function for a given URL rule. This does the same thing as add_url_rule but is intended for decorator usage:
@app.route('/') def index(): return 'Hello World'
- Parameters:
rule – the URL rule as string
options – the options to be forwarded to the underlying
werkzeug.routing.Ruleobject. A change to Werkzeug is handling of method options. methods is a list of methods this rule should be limited to (GET, POST etc.). By default a rule just listens for GET (and implicitly HEAD).
- run(import_string: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)¶
Run the application using uvicorn.
- Parameters:
import_string – application as import string (eg. “main:app”). This is needed to run using reload.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to uvicorn.run.
- test_client(**kwargs)¶
Creates a test client for this application. The keywords arguments passed in are passed to the
StarletteClient.
View a detailed reference of the FlaskApp
- class connexion.FlaskApp(import_name: str, *, lifespan: Optional[Callable[[Any], AbstractAsyncContextManager]] = None, middlewares: Optional[list] = None, server_args: Optional[dict] = None, specification_dir: Union[Path, str] = '', arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None)¶
Connexion Application based on ConnexionMiddleware wrapping a Flask application.
- Parameters:
import_name – The name of the package or module that this object belongs to. If you are using a single module, __name__ is always the correct value. If you however are using a package, it’s usually recommended to hardcode the name of your package there.
lifespan – A lifespan context function, which can be used to perform startup and shutdown tasks.
middlewares – The list of middlewares to wrap around the application. Defaults to
middleware.main.ConnexionMiddleware.default_middlewaresserver_args – Arguments to pass to the Flask application.
specification_dir – The directory holding the specification(s). The provided path should either be absolute or relative to the root path of the application. Defaults to the root path.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
swagger_ui_options – A
options.ConnexionOptionsinstance with configuration options for the swagger ui.pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – Instance of
options.ConnexionOptionswith configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAP.security_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERS
- add_api(specification: Union[Path, str, dict], *, base_path: Optional[str] = None, name: Optional[str] = None, arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None, **kwargs) Any¶
Register an API represented by a single OpenAPI specification on this application. Multiple APIs can be registered on a single application.
- Parameters:
specification – OpenAPI specification. Can be provided either as dict, a path to file, or a URL.
base_path – Base path to host the API. This overrides the basePath / servers in the specification.
name – Name to register the API with. If no name is passed, the base_path is used as name instead.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – A
options.ConnexionOptionsinstance with configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAPsecurity_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERSkwargs – Additional keyword arguments to pass to the add_api method of the managed middlewares. This can be used to pass arguments to middlewares added beyond the default ones.
- Returns:
The Api registered on the middleware application wrapping the framework.
- add_error_handler(code_or_exception: Union[int, Type[Exception]], function: Callable[[ConnexionRequest, Exception], Union[Awaitable[ConnexionResponse], ConnexionResponse]]) None¶
Register a callable to handle application errors.
- Parameters:
code_or_exception – An exception class or the status code of HTTP exceptions to handle.
function – Callable that will handle exception, may be async.
- add_middleware(middleware_class: Type[Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any], Callable[[], Awaitable[MutableMapping[str, Any]]], Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any]], Awaitable[None]]], Awaitable[None]]], position: MiddlewarePosition = MiddlewarePosition.BEFORE_CONTEXT, **options: Any) None¶
Add a middleware to the stack on the specified position.
- Parameters:
middleware_class – Middleware class to add
position – Position to add the middleware, one of the MiddlewarePosition Enum
options – Options to pass to the middleware_class on initialization
- add_url_rule(rule, endpoint: Optional[str] = None, view_func: Optional[Callable] = None, **options)¶
Connects a URL rule. Works exactly like the route decorator.
Basically this example:
@app.route('/') def index(): pass
Is equivalent to the following:
def index(): pass app.add_url_rule('/', 'index', index)
Internally`route` invokes add_url_rule so if you want to customize the behavior via subclassing you only need to change this method.
- Parameters:
rule – the URL rule as string.
endpoint – the name of the endpoint for the registered URL rule, which is used for reverse lookup. Flask defaults to the name of the view function.
view_func – the function to call when serving a request to the provided endpoint.
options – the options to be forwarded to the underlying
werkzeug.routing.Ruleobject. A change to Werkzeug is handling of method options. methods is a list of methods this rule should be limited to (GET, POST etc.). By default a rule just listens for GET (and implicitly HEAD).
- add_wsgi_middleware(middleware: Type[Callable[[Mapping[str, object], Union[Callable[[str, Sequence[Tuple[str, str]]], Callable[[bytes], Any]], Callable[[str, Sequence[Tuple[str, str]], Optional[Tuple[type, BaseException, TracebackType]]], Callable[[bytes], Any]]]], Iterable[bytes]]], **options: Any) None¶
Wrap the underlying Flask application with a WSGI middleware. Note that it will only be called at the end of the middleware stack. Middleware that needs to act sooner, needs to be added as ASGI middleware instead.
Adding multiple middleware using this method wraps each middleware around the previous one.
- Parameters:
middleware – Middleware class to add
options – Options to pass to the middleware_class on initialization
- route(rule: str, **options)¶
A decorator that is used to register a view function for a given URL rule. This does the same thing as add_url_rule but is intended for decorator usage:
@app.route('/') def index(): return 'Hello World'
- Parameters:
rule – the URL rule as string
options – the options to be forwarded to the underlying
werkzeug.routing.Ruleobject. A change to Werkzeug is handling of method options. methods is a list of methods this rule should be limited to (GET, POST etc.). By default a rule just listens for GET (and implicitly HEAD).
- run(import_string: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)¶
Run the application using uvicorn.
- Parameters:
import_string – application as import string (eg. “main:app”). This is needed to run using reload.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to uvicorn.run.
- test_client(**kwargs)¶
Creates a test client for this application. The keywords arguments passed in are passed to the
StarletteClient.
View a detailed reference of the ConnexionMiddleware
- class connexion.ConnexionMiddleware(app: Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any], Callable[[], Awaitable[MutableMapping[str, Any]]], Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any]], Awaitable[None]]], Awaitable[None]], *, import_name: Optional[str] = None, lifespan: Optional[Callable[[Any], AbstractAsyncContextManager]] = None, middlewares: Optional[List[Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any], Callable[[], Awaitable[MutableMapping[str, Any]]], Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any]], Awaitable[None]]], Awaitable[None]]]] = None, specification_dir: Union[Path, str] = '', arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None)¶
The main Connexion middleware, which wraps a list of specialized middlewares around the provided application.
- Parameters:
import_name – The name of the package or module that this object belongs to. If you are using a single module, __name__ is always the correct value. If you however are using a package, it’s usually recommended to hardcode the name of your package there.
middlewares – The list of middlewares to wrap around the application. Defaults to
middleware.main.ConnexionmMiddleware.default_middlewaresspecification_dir – The directory holding the specification(s). The provided path should either be absolute or relative to the root path of the application. Defaults to the root path.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – Instance of
options.ConnexionOptionswith configuration options for the swagger ui.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAP.security_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERS.
- add_api(specification: Union[Path, str, dict], *, base_path: Optional[str] = None, name: Optional[str] = None, arguments: Optional[dict] = None, auth_all_paths: Optional[bool] = None, jsonifier: Optional[Jsonifier] = None, pythonic_params: Optional[bool] = None, resolver: Optional[Union[Resolver, Callable]] = None, resolver_error: Optional[int] = None, strict_validation: Optional[bool] = None, swagger_ui_options: Optional[SwaggerUIOptions] = None, uri_parser_class: Optional[AbstractURIParser] = None, validate_responses: Optional[bool] = None, validator_map: Optional[dict] = None, security_map: Optional[dict] = None, **kwargs) None¶
Register een API represented by a single OpenAPI specification on this middleware. Multiple APIs can be registered on a single middleware.
- Parameters:
specification – OpenAPI specification. Can be provided either as dict, a path to file, or a URL.
base_path – Base path to host the API. This overrides the basePath / servers in the specification.
name – Name to register the API with. If no name is passed, the base_path is used as name instead.
arguments – Arguments to substitute the specification using Jinja.
auth_all_paths – whether to authenticate not paths not defined in the specification. Defaults to False.
jsonifier – Custom jsonifier to overwrite json encoding for json responses.
pythonic_params – When True, CamelCase parameters are converted to snake_case and an underscore is appended to any shadowed built-ins. Defaults to False.
resolver – Callable that maps operationId to a function or instance of
resolver.Resolver.resolver_error – Error code to return for operations for which the operationId could not be resolved. If no error code is provided, the application will fail when trying to start.
strict_validation – When True, extra form or query parameters not defined in the specification result in a validation error. Defaults to False.
swagger_ui_options – A dict with configuration options for the swagger ui. See
options.ConnexionOptions.uri_parser_class – Class to use for uri parsing. See
uri_parsing.validate_responses – Whether to validate responses against the specification. This has an impact on performance. Defaults to False.
validator_map – A dictionary of validators to use. Defaults to
validators.VALIDATOR_MAPsecurity_map – A dictionary of security handlers to use. Defaults to
security.SECURITY_HANDLERSkwargs – Additional keyword arguments to pass to the add_api method of the managed middlewares. This can be used to pass arguments to middlewares added beyond the default ones.
- Returns:
The Api registered on the wrapped application.
- add_error_handler(code_or_exception: Union[int, Type[Exception]], function: Callable[[ConnexionRequest, Exception], Union[Awaitable[ConnexionResponse], ConnexionResponse]]) None¶
Register a callable to handle application errors.
- Parameters:
code_or_exception – An exception class or the status code of HTTP exceptions to handle.
function – Callable that will handle exception, may be async.
- add_middleware(middleware_class: Type[Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any], Callable[[], Awaitable[MutableMapping[str, Any]]], Callable[[MutableMapping[str, Any]], Awaitable[None]]], Awaitable[None]]], *, position: MiddlewarePosition = MiddlewarePosition.BEFORE_CONTEXT, **options: Any) None¶
Add a middleware to the stack on the specified position.
- Parameters:
middleware_class – Middleware class to add
position – Position to add the middleware, one of the MiddlewarePosition Enum
options – Options to pass to the middleware_class on initialization
- default_middlewares = [<class 'connexion.middleware.server_error.ServerErrorMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.exceptions.ExceptionMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.swagger_ui.SwaggerUIMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.routing.RoutingMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.request_validation.RequestValidationMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.response_validation.ResponseValidationMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.lifespan.LifespanMiddleware'>, <class 'connexion.middleware.context.ContextMiddleware'>]¶
- run(import_string: Optional[str] = None, **kwargs)¶
Run the application using uvicorn.
- Parameters:
import_string – application as import string (eg. “main:app”). This is needed to run using reload.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to uvicorn.run.